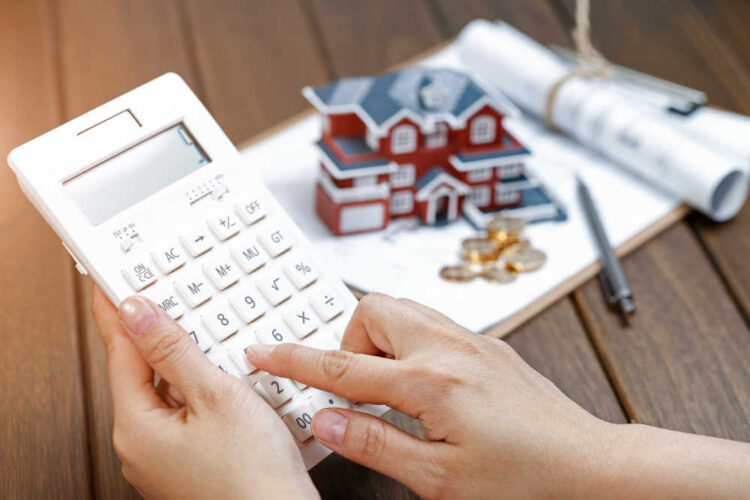
Buying a home is a significant financial commitment, and securing a loan is a crucial step. While borrowing helps in purchasing a property, understanding the repayment structure is equally important. Interest on loans can add up quickly, affecting overall affordability. That’s why knowing how banks compute interest charges is essential for financial planning.
How to calculate interest on a home loan is a common concern among borrowers looking for clarity. Different factors influence the amount paid over time, including loan type, tenure, and interest rates. Miscalculations can lead to unexpected costs, so proper evaluation is vital. By understanding these elements, homeowners can make informed decisions and manage repayments effectively.
Fixed vs. Floating Interest Rates
Home loan interest comes in two primary forms: fixed and floating rates. Each option impacts repayments differently and suits different financial strategies. Choosing the right one requires assessing long-term financial goals and market trends.
Fixed-rate loans maintain the same percentage throughout the tenure. This stability makes budgeting easier but often comes with higher rates. Alternatively, market forces determine the movement of floating interest rates. While they may start lower, they can increase unexpectedly, affecting monthly payments.
Understanding Simple vs. Compound Interest
Lenders calculate interest using different methods, which affect the total repayment amount. The most common approaches are simple and compound calculations. Borrowers should understand both methods to avoid surprises when reviewing loan agreements.
Simple interest applies a fixed percentage to the principal amount. It remains constant over time, leading to predictable payments. Compound interest, however, accrues on both the principal and previously accumulated interest. This results in higher payments over the loan term, significantly increasing total costs.
EMI Calculation: Breaking Down Payments
The building blocks of house loan repayments are Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs). Lenders calculate these fixed monthly payments using a standard formula. Understanding EMI structures helps borrowers assess affordability and better plan their finances.
The EMI formula considers the principal, rate of interest, and loan tenure. Longer tenures reduce monthly payments but increase the total paid. More extended repayment periods save money in the long run but come with larger monthly payments. Online EMI calculators simplify this process and provide instant estimates.
Factors That Influence Loan Interest Costs
Several elements determine the total interest paid on a home loan. Borrowers should evaluate these factors before committing to long-term financial obligations. Even minor changes in any of these variables can significantly impact overall costs. Loan tenure plays a crucial role in determining expenses.
Longer tenures increase the total amount paid, even if the monthly outlay seems manageable. Lenders base their interest rates in part on borrowers’ credit scores. Higher scores result in better loan terms, reducing overall borrowing costs. Lenders also consider the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio, which influences credit approval and rates.
Tips to Reduce Interest Costs on Your Loan
Borrowers can take proactive steps to minimize interest expenses. A well-planned repayment strategy can lead to substantial long-term savings, and simple changes in financial habits can make a noticeable difference. Making extra payments reduces the principal faster, lowering the burden.
Choosing a shorter loan tenure can also reduce costs. Negotiating better rates with lenders based on a strong credit history may result in more favorable terms. Making a larger down payment upfront can further decrease the amount, reducing overall expenses.
Knowing how to calculate interest on a home loan is a crucial skill for managing borrowing costs effectively. Borrowers who stay informed can save money and avoid financial strain. Tracking payments and leveraging prepayment options enhance financial stability. Making informed choices today ensures a secure and manageable loan experience in the future.