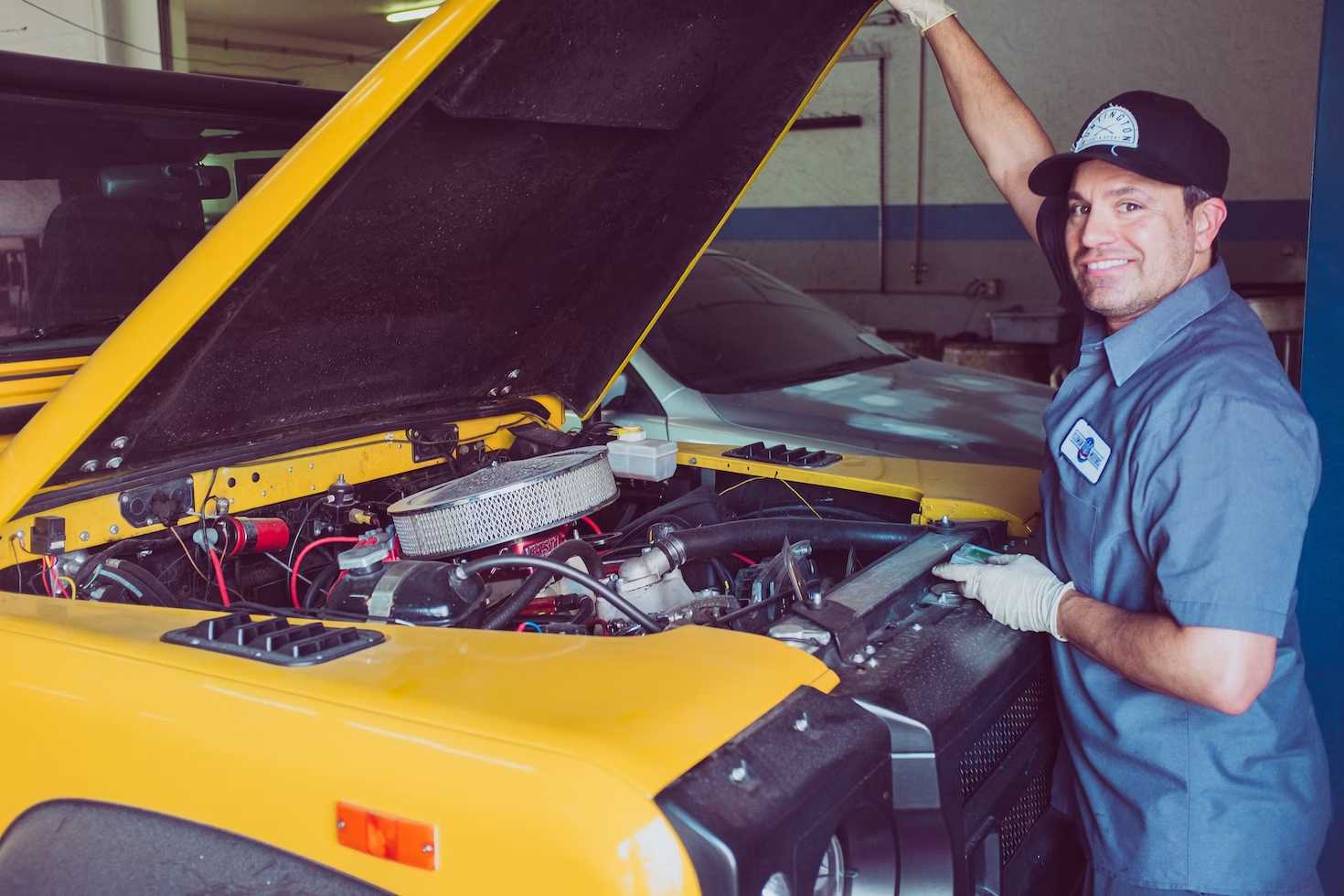
Automotive service technicians specialize in diagnosing automobile problems. By applying their knowledge and experience to each situation, these service professionals can determine whether a vehicle requires repair, maintenance or modification services.
Automobile inspectors act like detectives, searching for evidence in vehicles. They may use special test equipment and often work in uncomfortable positions with dirty parts and tools. If you’re having problems in Abbotsford but are too nervous to ask for help (or perhaps even thinking of becoming one, yourself) – read the following article for a more in-depth look at the automotive repair industry.
Mechanics
Auto mechanics specialize in diagnosing mechanical issues, repairing or replacing defective parts, keeping detailed records of their work performed, as well as general maintenance such as oil changes, tire rotations and inspections. They may specialize in certain areas like front-end repairs, brakes or air-conditioning and heating systems – in addition to having strong technical expertise they must also have strong customer service abilities in order to communicate clearly with customers about complex technical issues and explain any complications effectively.
Mechanists have numerous opportunities to acquire their trade, from on-the-job training and apprenticeship programs, to postsecondary education. Some vocational schools and colleges provide programs accredited by the National Automotive Technicians Education Foundation (NATEF), with intensive career preparation lasting six months to one year and awarding certificates upon graduation.
Experienced technicians may be sent to manufacturer-sponsored training centers in order to expand their knowledge or acquire specific component repair techniques. For example, automotive technicians specializing in fixing air conditioning must receive specific training in handling and disposing of refrigerants properly.
As cars increasingly adopt advanced computer systems, mechanics must remain knowledgeable of new technology and continually sharpen their skills. Auto mechanics frequently work with potentially hazardous tools and equipment as well as chemicals, solvents, and particulates which must all be handled carefully to avoid injuries to themselves or customers.
Service Bays
Repair bays provide auto mechanics with all the equipment and tools necessary for them to repair vehicles, making an organized workspace integral to their work and customers’ safety. A tidy workspace helps technicians gain easy access to parts and tools they need quickly while also helping reduce risks to expensive equipment while eliminating distractions caused by customers waiting their turn for repair services.
Recent years have witnessed a steady decrease in service bays. A study conducted by Digital Dealer revealed that there are now 50,000 fewer bays nationwide compared to 10 years ago – https://www.marketsource.com/blog/shortage-of-auto-technicians/. Whether this trend can be explained by lack of qualified technicians or declining demand for car repairs, many shops are decreasing the number of stalls they make available for repair work.
As you determine what job or jobs you’ll need a technician to do, remember that an experienced tech who specializes in transmissions, engine rebuilding or brakes will require more money and planning ahead than if they were performing simple maintenance jobs such as oil changes and tune-ups.
Tools
Mechanics need numerous tools in order to work safely and efficiently, from using the appropriate tool for every job to reducing accidents and vehicle damage risks with proper equipment. While quality tools may cost more upfront, they will last longer with reduced maintenance needs than their cheaper alternatives; financing solutions may be available if purchasing professional-grade tools is what’s needed for their repair shop.
Volt-ohm meters or multimeters are important tools for automotive mechanics. These handheld devices measure electrical voltage and current to help identify problems with wiring or power supplies in vehicles, as well as check for voltage presence in fuses, switches, or relays.
Jumper cables are another tool in the toolbox of every mechanic, as they enable them to reconnect a dead battery to another vehicle, helping start its engine and improve roadside safety. A basic code reader (which you can learn about here) is another essential diagnostic device; this tool connects directly with a vehicle’s computer system and reads error codes that help pinpoint issues quickly for repairs to be completed correctly.
Equipment
Automotive mechanics use an arsenal of tools and equipment to repair vehicles. Their duties may include inspection and maintenance services, troubleshooting issues, making repairs to components such as engines, transmissions, brakes and electrical systems and installing new parts or accessories as necessary.
Automotive service technicians typically work in well-equipped repair shops that feature customer waiting areas and office tasks for office tasks; computer stations to access information; parts departments where parts may be obtained for vehicle repairs.
Effective communication among mechanics is of utmost importance in their field, so effective dialogue between team members must take place between mechanics. They should be able to explain technical details of vehicle repair in terms that customers can understand while providing accurate cost estimates for work they plan to complete and swiftly addressing customer concerns quickly and effectively.
Auto mechanics rely on advanced diagnostic equipment in addition to traditional tools and equipment when diagnosing vehicle issues, including computerized testing devices that compare test results against benchmarked standards provided by vehicle manufacturers. This information allows them to identify specific issues quickly and make necessary repairs.

Safety
Mechanics work with dangerous machinery, chemicals and tools that put them at a greater risk of workplace accidents. Any auto mechanic in Abbotsford has finished safety training programs for their specific areas, but accidents do happen. Work-related injuries can reduce productivity in auto repair shops as well as increase medical costs; to minimize these injuries and keep employees safe at work.
Not only do mechanics need specialized equipment, they must also keep detailed records of repairs and services performed. Most often they use software programs for this task. Doing this helps avoid mistakes while providing valuable information for future customers.
Fire hazards in automotive shops are an all too familiar hazard that can result in serious injuries for technicians. Fire extinguishers must be easily accessible and clearly labeled to identify their purpose; regularly test fire alarms; and ensure electrical systems aren’t exposed to flammable materials.
Strains and pulls are among the most frequently reported injuries in automotive repair shops, often as a result of improper posture, heavy lifting or fatigue. To minimize their incidence, mechanics usually stretch and flex before beginning work as well as maintain a healthy diet with limited alcoholic drinks to reduce any drowsiness caused by over-drinking.